OBJECTIVE
Students will understand what a perennial forest is and how to best choose plants that benefit the ecosystem.
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS
How does a forest ecosystem function? What is ecosystem mimicry? What kinds of resources do forests provide for humans? What is the role of humans in forests?
MATERIALS NEEDED
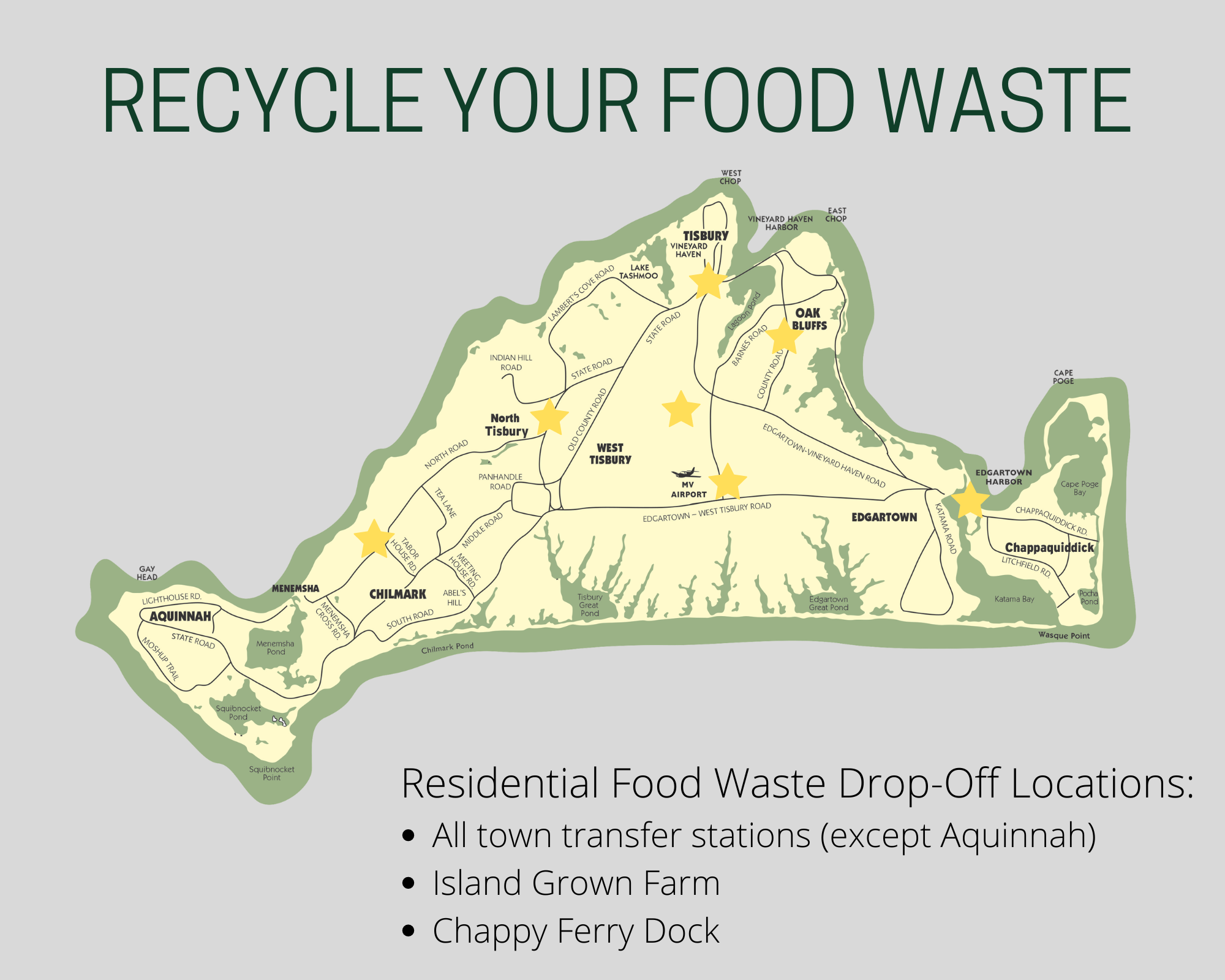
“perennial forest gardens” slideshow, tree chart worksheets, chrome book cart for research, forest garden crop worksheet
Books: Farming the Woods, Paradise Lot, Edible Forest Gardens: Volumes I and II
PROCEDURE
Introduction: Imagine yourself in a forest you’ve been to on the island. What do you see? What are the components of the forest ecosystem?
Soil: growing medium, environment for decomposers, holds water
Decomposers (including fungi and bacteria): break down nutrients for plants
Trees: Take in CO2 and produce Oxygen, food, capture water, roots hold soil in place
Bushes: provide food, also photosynthesize, cover fresh areas quickly
Ground covers and layers of debris: cover the soil, protect decomposition process and protect from erosion, capture water
Birds: fertilize, keep insects and smaller mammals in check
Mammals: fertilize, predators keep herbivores in check
Insects: predators prey on herbivores, keep them in check
Stream: water source, fish habitat, food source
What does each of these components do for the system? (Use notes above)
Explain:
Edible Forest Gardening is about mimicking the natural system of the forest in a garden, but using crops that we want for food, shelter, soil building, and medicine.
Two methods:
- Planting a garden LIKE the woods (ground cover, bushes, trees)
- Planting a garden IN the woods (like shiitake mushrooms and ginseng)
Show slideshow of examples
Activity: Gather information for 1 tree species, 1 bush, and 1 ground cover that you are interested in growing in our garden, using the forest garden crop worksheet.
FOLLOW UP & EXTENSIONS
Field trip to Thimble Farm Orchard
Field trip: foraging on MV
Film: Restoration Agriculture, Mark Shepard, 30 minutes